1. 虚拟列表
原理
- 设置一个可视区域,然后用户在滚动列表的时候,本质上是动态修改可视区域里面的内容
技术细节
动态修改可以采用动态截断数组数据的操作来实现,因此需要得到一些信息:
- 可视区域起始数据索引(startIndex)
- 可视区域结束数据索引(endIndex)
- 可视区域的数据,利用上述的startIndex和endIndex截断
- 整个列表中的偏移位置 startOffset
简单实现:假设每一项定高
如下图所示:
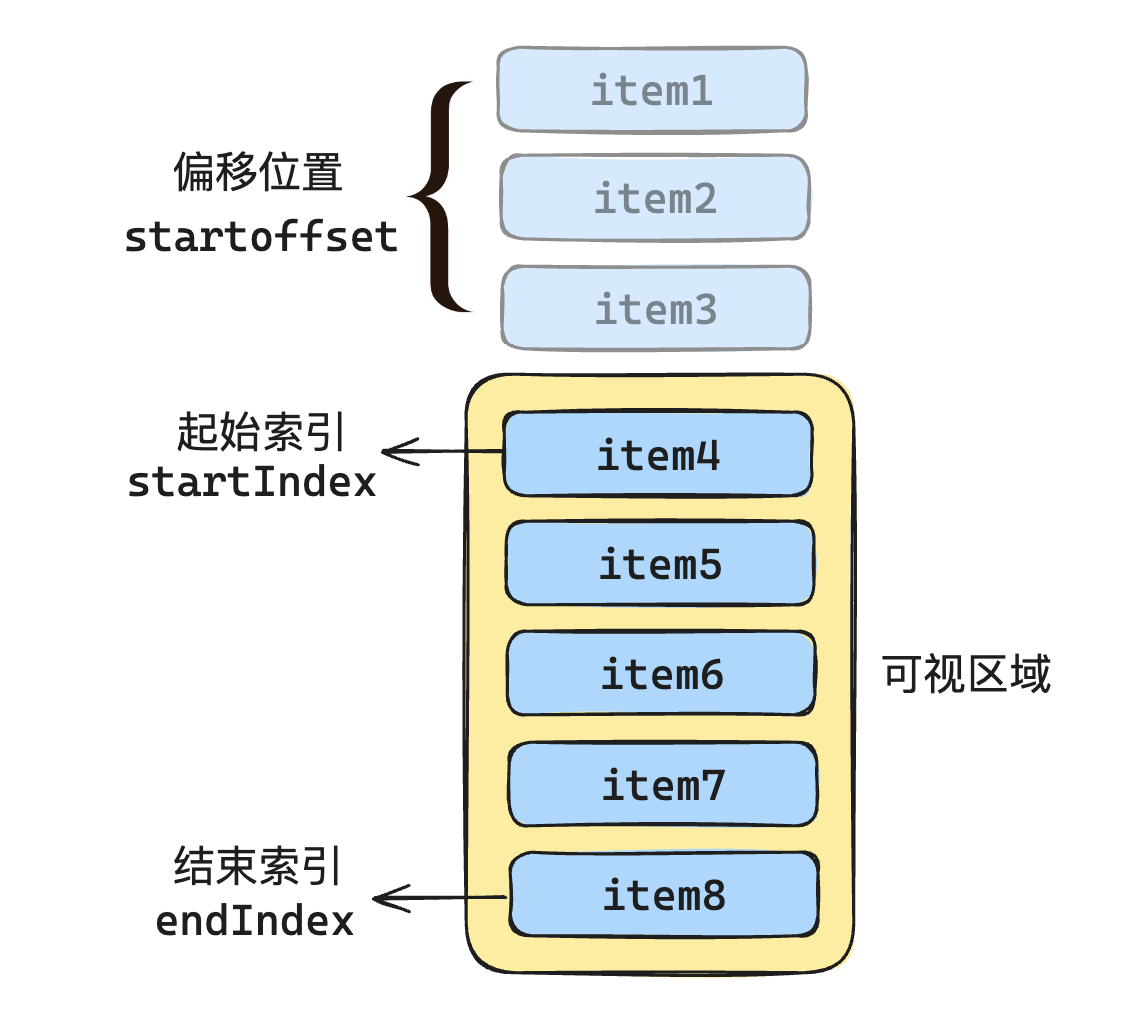
整个虚拟列表的设计如下:
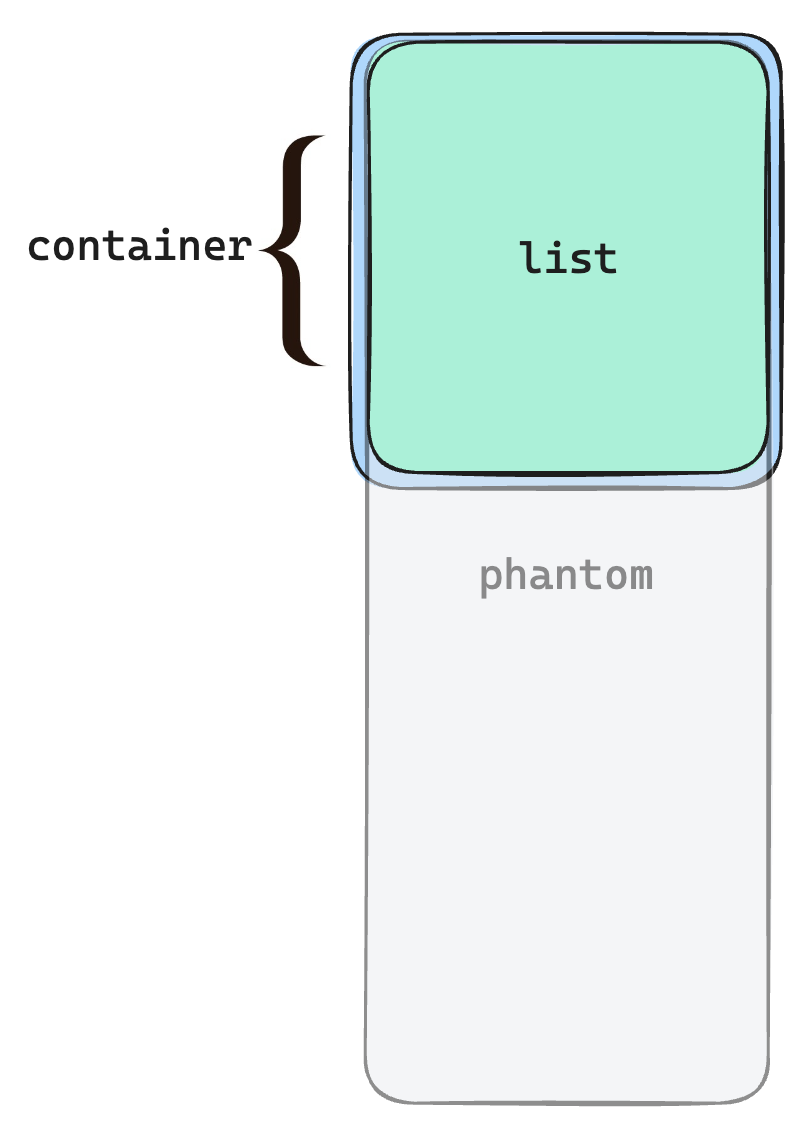
<!-- 可视区域容器 -->
<div class="infinite-list-container">
<!-- 这是容器里面的占位,高度是总列表高度,用于形成滚动条 -->
<div class="infinite-list-phantom"></div>
<!-- 列表项渲染区域 -->
<div class="infinite-list">
<!-- item-1 -->
<!-- item-2 -->
<!-- ...... -->
<!-- item-n -->
</div>
</div><!-- 可视区域容器 -->
<div class="infinite-list-container">
<!-- 这是容器里面的占位,高度是总列表高度,用于形成滚动条 -->
<div class="infinite-list-phantom"></div>
<!-- 列表项渲染区域 -->
<div class="infinite-list">
<!-- item-1 -->
<!-- item-2 -->
<!-- ...... -->
<!-- item-n -->
</div>
</div>- infinite-list-container: 可视区域容器
- infinite-list-phantom: 这是容器里面的占位,高度是总列表高度,用于形成滚动条
- infinite-list:列表项渲染区域
如下图所示:
接下来监听 infinite-list-container 的 scroll 事件,获取滚动位置的 scrollTop
- 假定可视区域高度固定,称之为 screenHeight
- 假定列表每项高度固定,称之为 itemSize
- 假定列表数据称之为 listData
- 假定当前滚动位置称之为 scrollTop
那么我们能够计算出这么一些信息:
- 列表总高度 listHeight = listData.length * itemSize
- 可显示的列表项数 visibleCount = Math.ceil(screenHeight / itemSize)
- 数据的起始索引 startIndex = Math.floor(scrollTop / itemSize)
- 数据的结束索引 endIndex = startIndex + visibleCount
- 列表显示数据为 visibleData = listData.slice(startIndex, endIndex)
当发生滚动之后,由于渲染区域相对于可视区域发生了偏移。我们需要计算出来这个偏移量,然后使用 transform 将 list 重新移回到可视区域。
偏移量 startOffset = scrollTop - (scrollTop % itemSize)
优化点1:动态高度,每一项内容不定高
细节
- 在实际渲染之前是很难拿到每一项的真实高度的,那么要如何获取每一项的高度?
- 由于内容不定高,那么之前基于定高的计算信息则全部失效,那么如何重新基于不定高的方式去计算?
- 既然计算信息发生了变更,那么列表渲染方式有何改变?
解决方案
问题1:采用预估的方式
具体做法:创建一个缓存列表,其中列表项字段为 索引、高度与定位,并预估列表项高度(estimatedItemSize)用于初始化缓存列表,在渲染后根据 DOM 实际情况更新缓存列表和设置真实高度
问题2:新的计算信息
具体做法:
列表总高度:首次渲染:listHeight = listData.length * estimatedItemSize ,后续渲染:缓存列表最后一项的定位字段的值
jsconst updateItemsSize = () => { let nodes = items.value as HTMLElement[] nodes.forEach((node) => { let rect = node.getBoundingClientRect() let height = rect.height let index = +node.id.slice(1) let oldHeight = positions.value[index].height let dValue = oldHeight - height if (dValue) { positions.value[index].bottom = positions.value[index].bottom - dValue positions.value[index].height = height for (let k = index + 1; k < positions.value.length; k++) { positions.value[k].top = positions.value[k - 1].bottom positions.value[k].bottom = positions.value[k].bottom - dValue } } }) }const updateItemsSize = () => { let nodes = items.value as HTMLElement[] nodes.forEach((node) => { let rect = node.getBoundingClientRect() let height = rect.height let index = +node.id.slice(1) let oldHeight = positions.value[index].height let dValue = oldHeight - height if (dValue) { positions.value[index].bottom = positions.value[index].bottom - dValue positions.value[index].height = height for (let k = index + 1; k < positions.value.length; k++) { positions.value[k].top = positions.value[k - 1].bottom positions.value[k].bottom = positions.value[k].bottom - dValue } } }) }可显示的列表项数:visibleCount = Math.ceil(screenHeight / estimatedItemSize )
数据的起始索引:在缓存列表中搜索第一个底部定位大于列表垂直偏移量的列表项,然后返回其索引
jsconst binarySearch = (list: any[], value: number) => { let start = 0 let end = list.length - 1 let tempIndex = null while (start <= end) { let midIndex = Math.floor((start + end) / 2) let midValue = list[midIndex].bottom if (midValue === value) { return midIndex + 1 } else if (midValue < value) { start = midIndex + 1 } else if (midValue > value) { if (tempIndex === null || tempIndex > midIndex) { tempIndex = midIndex } end = midIndex - 1 } } return tempIndex }const binarySearch = (list: any[], value: number) => { let start = 0 let end = list.length - 1 let tempIndex = null while (start <= end) { let midIndex = Math.floor((start + end) / 2) let midValue = list[midIndex].bottom if (midValue === value) { return midIndex + 1 } else if (midValue < value) { start = midIndex + 1 } else if (midValue > value) { if (tempIndex === null || tempIndex > midIndex) { tempIndex = midIndex } end = midIndex - 1 } } return tempIndex }这个缓存列表是一个有序的数组,那么使用二分查找效率会更高一些,时间复杂度相比之前的 O(n) 优化为了 O(logN)
问题3:用于渲染页面元素的数据是根据 开始/结束索引 在 数据列表 中截断出来的,所以只要保证索引的正确计算,那么渲染方式是无需变化的
优化点2:滚动过快的白屏闪烁
添加缓存区,整个渲染区域由 可视区 + 缓冲区 共同组成
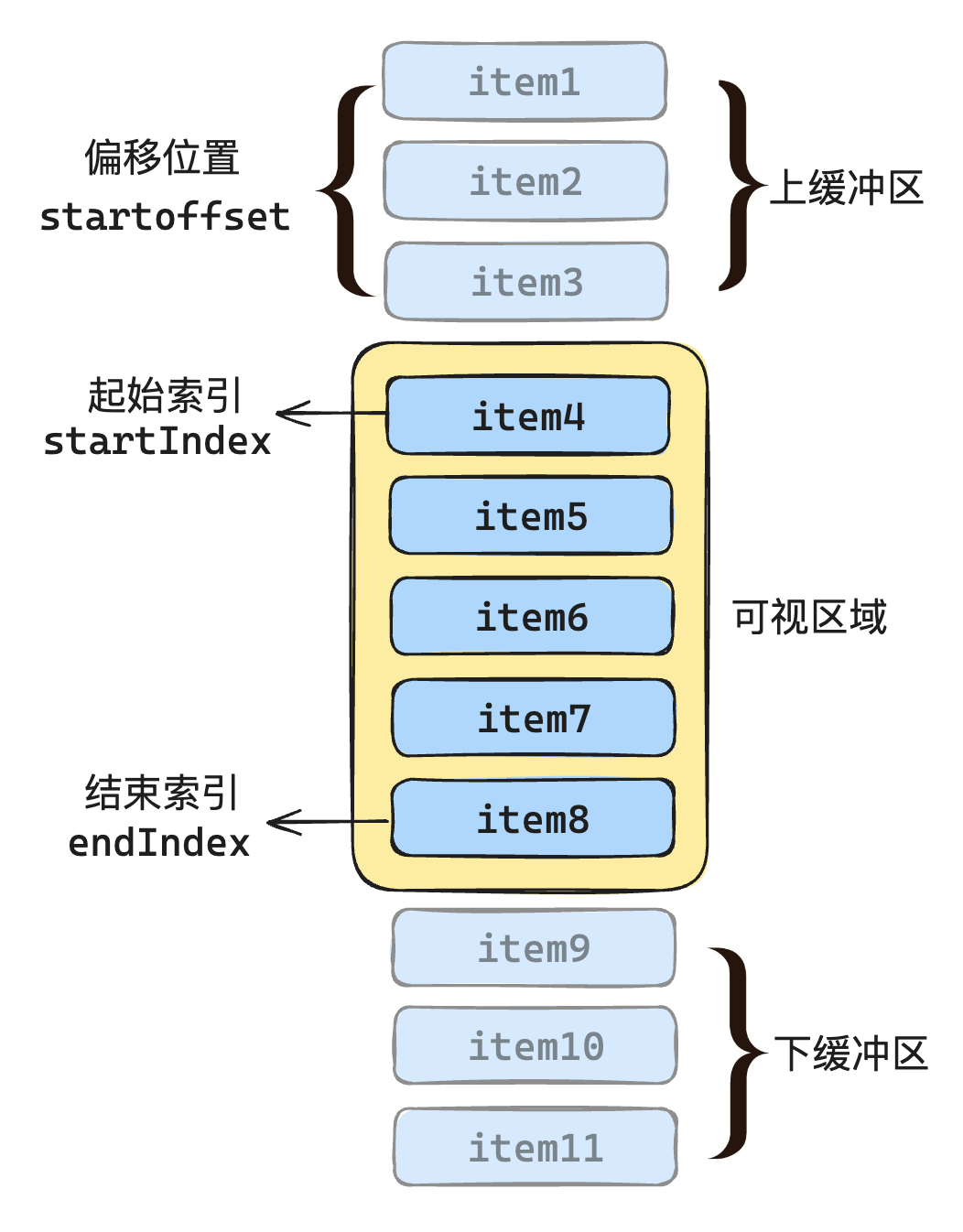
具体做法
增加一个 props 叫做 bufferScale,用于接收缓冲区数据和可视区域数据的一个比例
jsconst props = defineProps({ // ... bufferScale: { type: Number, default: 1 }, // ... })const props = defineProps({ // ... bufferScale: { type: Number, default: 1 }, // ... })接下来就可以根据这个比例,计算出上下缓冲区的数量:
js// 上方缓冲区 const aboveCount = computed(() => { return Math.min(start.value, props.bufferScale * visibleCount.value) }) // 下方缓冲区 const belowCount = computed(() => { return Math.min(props.listData.length - end.value, props.bufferScale * visibleCount.value) })// 上方缓冲区 const aboveCount = computed(() => { return Math.min(start.value, props.bufferScale * visibleCount.value) }) // 下方缓冲区 const belowCount = computed(() => { return Math.min(props.listData.length - end.value, props.bufferScale * visibleCount.value) })现在 visibleData 的计算也需要更新,需要加入上下缓冲区
jsconst visibleData = computed(() => { let startIdx = start.value - aboveCount.value let endIdx = end.value + belowCount.value return _listData.value.slice(startIdx, endIdx) })const visibleData = computed(() => { let startIdx = start.value - aboveCount.value let endIdx = end.value + belowCount.value return _listData.value.slice(startIdx, endIdx) })另外偏移量的计算也需要更新,需要将缓冲区考虑进去:
jsconst setStartOffset = () => { let startOffset if (start.value >= 1) { let size = positions.value[start.value].top - (positions.value[start.value - aboveCount.value] ? positions.value[start.value - aboveCount.value].top : 0) startOffset = positions.value[start.value - 1].bottom - size } else { startOffset = 0 } content.value.style.transform = `translate3d(0,${startOffset}px,0)` }const setStartOffset = () => { let startOffset if (start.value >= 1) { let size = positions.value[start.value].top - (positions.value[start.value - aboveCount.value] ? positions.value[start.value - aboveCount.value].top : 0) startOffset = positions.value[start.value - 1].bottom - size } else { startOffset = 0 } content.value.style.transform = `translate3d(0,${startOffset}px,0)` }